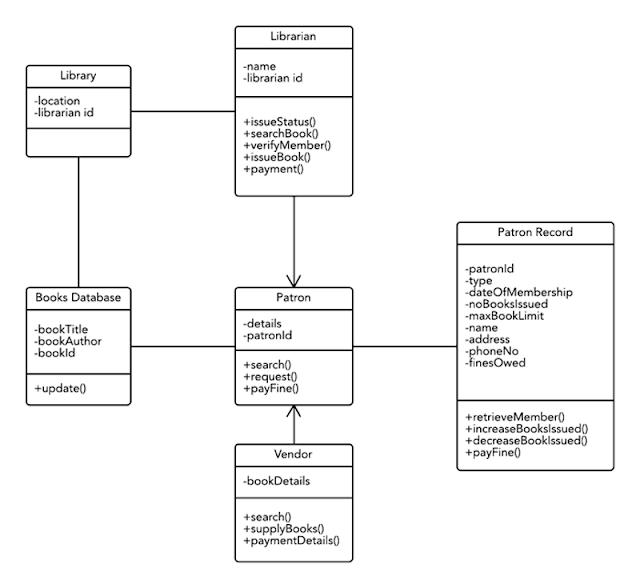
2016 – 2017 Assignment Question
Class diagram
In software engineering, a class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system’s classes, their attributes, operations (or methods), and the relationships among objects.
- Classes
Classes represent an abstraction of entities with common characteristics. Associations represent the relationships between classes.
- Active Classes
Active classes initiate and control the flow of activity, while passive classes store data and serve other classes. Illustrate active classes with a thicker border.
- Visibility
Use visibility markers to signify who can access the information contained within a class. Private visibility, denoted with a – sign, hides information from anything outside the class partition. Public visibility, denoted with a + sign, allows all other classes to view the marked information. Protected visibility, denoted with a # sign, allows child classes to access information they inherited from a parent class.
- Associations
Associations represent static relationships between classes. Place association names above, on, or below the association line. Use a filled arrow to indicate the direction of the relationship.
- Multiplicity (Cardinality)
Place multiplicity notations near the ends of an association.
- Constraint
Place constraints inside curly braces {}.
- Composition and Aggregation
Composition is a special type of aggregation that denotes a strong ownership between Class A, the whole, and Class B, its part. Illustrate composition with a filled diamond.
- Generalization
Generalization is another name for inheritance or an “is a” relationship.
 |
| Image source https://www.lucidchart.com/pages/class-diagram-for-library-management-system-UML |