Linear Search Algorithm | Example | Time Complexity
Searching-
- Searching is a process of finding a particular element among several given elements.
- The search is successful if the required element is found.
- Otherwise, the search is unsuccessful.
Searching Algorithms-
Searching Algorithms are a family of algorithms used for the purpose of searching.
The searching of an element in the given array may be carried out in the following two ways-

- Linear Search
- Binary Search
In this article, we will discuss about Linear Search Algorithm
Linear Search-
- Linear Search is the simplest searching algorithm.
- It traverses the array sequentially to locate the required element.
- It searches for an element by comparing it with each element of the array one by one.
- So, it is also called as Sequential Search.
Linear Search Algorithm is applied when-
- No information is given about the array.
- The given array is unsorted or the elements are unordered.
- The list of data items is smaller.
Linear Search Algorithm-
Consider-
- There is a linear array ‘a’ of size ‘n’.
- Linear search algorithm is being used to search an element ‘item’ in this linear array.
- If search ends in success, it sets loc to the index of the element otherwise it sets loc to -1.
Then, Linear Search Algorithm is as follows-
Linear_Search (a , n , item , loc)
Begin
for i = 0 to (n – 1) by 1 do
if (a[i] = item) then
set loc = i
Exit
endif
end for
set loc = -1
End
Time Complexity Analysis-
Linear Search time complexity analysis is done below-
Best case-
In the best possible case,
- The element being searched may be found at the first position.
- In this case, the search terminates in success with just one comparison.
- Thus in best case, linear search algorithm takes O(1) operations.
Worst Case-
In the worst possible case,
- The element being searched may be present at the last position or not present in the array at all.
- In the former case, the search terminates in success with n comparisons.
- In the later case, the search terminates in failure with n comparisons.
- Thus in worst case, linear search algorithm takes O(n) operations.
Thus, we have-
Linear Search Efficiency-
- Linear Search is less efficient when compared with other algorithms like Binary Search & Hash tables.
- The other algorithms allow significantly faster searching.
Linear Search Example-
Consider-
- We are given the following linear array.
- Element 15 has to be searched in it using Linear Search Algorithm.
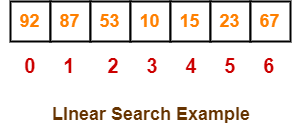
Now,
- Linear Search algorithm compares element 15 with all the elements of the array one by one.
- It continues searching until either the element 15 is found or all the elements are searched.
Linear Search Algorithm works in the following steps-
Step-01:
- It compares element 15 with the 1st element 92.
- Since 15 ≠ 92, so required element is not found.
- So, it moves to the next element.
Step-02:
- It compares element 15 with the 2nd element 87.
- Since 15 ≠ 87, so required element is not found.
- So, it moves to the next element.
Step-03:
- It compares element 15 with the 3rd element 53.
- Since 15 ≠ 53, so required element is not found.
- So, it moves to the next element.
Step-04:
- It compares element 15 with the 4th element 10.
- Since 15 ≠ 10, so required element is not found.
- So, it moves to the next element.
Step-05:
- It compares element 15 with the 5th element 15.
- Since 15 = 15, so required element is found.
- Now, it stops the comparison and returns index 4 at which element 15 is present